What is Hepatitis B ?
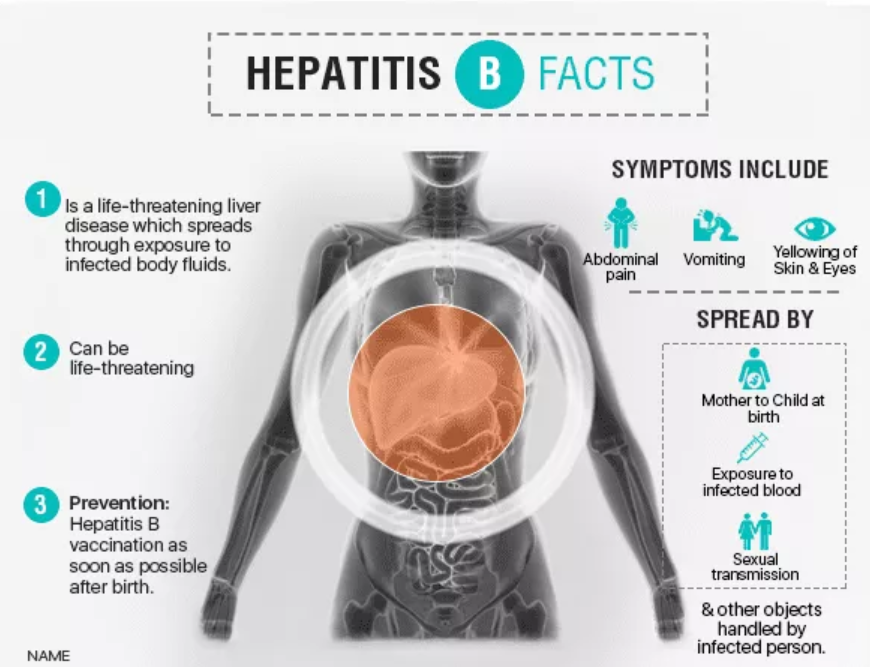
Over 350 million people in the world are infected with Hepatitis B, out of which 47 million alone are in India. Hepatitis B is a critical (life-threatening) liver infection caused by hepatitis B virus (HBV). It can give rise to other liver-related severe infections & put infected people at high risk of mortality from cirrhosis and liver cancer. This virus mainly spreads from exposure to infected body fluids, such as blood and semen. The virus can also spread from mother to the infant during birth (perinatal transmission) or through sexual transmission, particularly in unvaccinated men who have intercourse with multiple partners.
What are the Symptoms of Hepatitis B ?
- Fatigue, Nausea & Vomiting
- Pain or discomfort in Abdomen, especially in the right area beneath lower ribs
- Clay-colored Bowel movements
- Loss of Appetite
- Dark Urine
- Yellowing of the skin and Eyes (Jaundice).
Those with acute HBV infection may develop Acute Liver Failure, which can later lead to Mortality. Patients with Chronic Liver Infection may develop liver Cirrhosis or Liver Cancer.
Who is at risk for chronic disease ?
Infants and children:
- 80–90% of infants infected with HBV during the 1st year of life develop chronic infections
- 30–50% of children below the age of 6 years develop chronic infections.
Adults:
- 5% of otherwise fit & healthy people develop chronic infections
- Around 20–30% of chronically infected adults develop cirrhosis and/or liver cancer.
How is Hepatitis B diagnosed ?
Although Hepatitis B cannot be differentiated from other Hepatitis virus clinically, a number of blood tests are available to diagnose & distinguish acute and chronic Hepatitis B infections.
- Acute Hepatitis B infection: Characterized by the presence of HBsAg and IgM antibody to the core antigen, HBcAg. The presence of Hepatitis Be antigen (HBeAg) suggests that whether or not, the blood and other body fluids of the patient are contagious.
- Chronic Hepatitis B infection: Characterized by the presence of HBsAg for at least 6 months (with or without HBeAg). The presence of HBsAg suggests the risk for developing chronic liver disease and liver cancer.
What is the treatment ?
Chronic Hepatitis B infection can be treated by reducing HBV DNA level and maintain it at lowest possible levels for histological improvement and ALT/AST normalisation drugs. Those with chronic infection can be treated with drugs, including oral antiviral agents. Drugs preferred for treatment are peggylated interferons and oral antivirals like lamivudine, adefovir, tenofovir and entecavir. This Treatment can slow the progression of cirrhosis, reduce incidence of liver cancer and improve long term survival. Book your appointment with one of the best liver surgeons in India, Dr. Vivek Vij.